Text adapted from "The patient who is depressed" in Psychiatry in primary care by Raymond W. Lam, (CAMH, 2019).
Both pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy are effective treatments for depression. Treatment choice depends on the acuity and severity of the depression.
Measurement-based care
Measurement-based care involves collecting patient data throughout treatment to inform clinical care. It can be used with any treatment modality, and has been found to improve treatment outcomes for depression in primary care (Yeung et al., 2012).
To track outcomes and support clinical decision making, use validated symptom questionnaires such as the PHQ-9 and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale (GAD-7). Patients can complete these questionnaires at home or in the waiting room. In addition to being a screening and diagnostic aid, the PHQ-9 is useful for monitoring treatment response.
Throughout treatment, assess functional impairment and improvements using validated scales such as the Sheehan Disability Scale, which assesses general functioning, and the Lam Employment Absence and Productivity Scale (LEAPS), which assesses occupational functioning.
MoodFx.ca is a free, mobile-optimized tool that supports measurement- based care. Patients can monitor and track their depressive symptoms and functioning using validated questionnaires. MoodFx includes the PHQ-9, GAD-7 and LEAPS, as well as side-effect burden and functional scales.
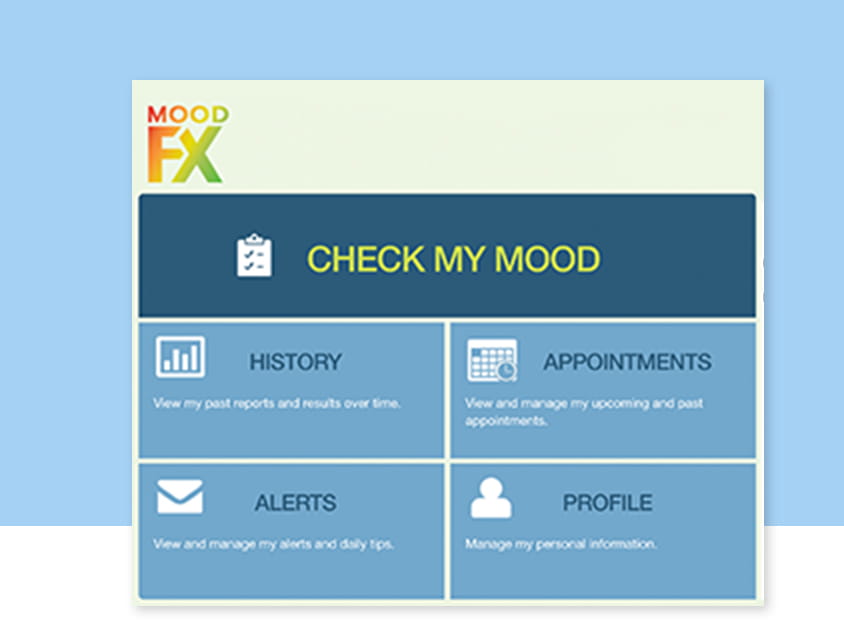
MoodFX
This free, mobile-optimized tool supports measurement- based care. Patients can monitor and track their depressive symptoms and functioning using validated questionnaires.
In Depression